Is Orf A Rare And Devastating Disease In Goats And Sheep? Yes! A contagious viral disease that affects sheep and goats, Orf is a contagious viral disease that affects sheep and goats.
Editor's Notes: "Orf: A Rare And Devastating Disease In Goats And Sheep" have published today date.
This topic is important to read because Orf is a highly contagious disease that can cause significant economic losses to goat and sheep producers. There is no specific treatment for Orf, but the disease can be prevented by vaccination.
Our team have made some analysis and have digged out the information about Orf: A Rare And Devastating Disease In Goats And Sheep. Here is what we found out!
Key differences or Key takeaways:
| Feature | Orf |
|---|---|
| Causative agent | Orf virus |
| Species affected | Sheep and goats |
| Clinical signs | Sores on the lips, nose, and teats |
| Treatment | None |
| Prevention | Vaccination |
FAQ
Orf, also known as contagious ecthyma, is a highly contagious viral disease that affects goats and sheep. It is caused by the orf virus, which is a member of the poxvirus family. Orf is characterized by the development of scabs and lesions on the skin, particularly around the mouth, nose, and feet. The disease can cause significant discomfort and economic losses to farmers.

En images : l’Alberta, au Canada, ravagée par des incendies sans précédent - Source www.parismatch.com
Question 1: What are the symptoms of orf?
The most common symptom of orf is the development of scabs and lesions on the skin. These lesions typically start as small, red bumps that gradually enlarge and develop a scab. The scabs can be painful and itchy, and they can cause the animal to lose its appetite and become depressed. In severe cases, orf can lead to secondary infections, such as pneumonia or septicemia.
Question 2: How is orf transmitted?
Orf is transmitted through direct contact with an infected animal or through contact with contaminated objects, such as shared food or water bowls. The virus can also be transmitted through the air, over short distances.
Question 3: How is orf treated?
There is no specific treatment for orf. The disease typically runs its course in 2-3 weeks. However, supportive care can be provided to help relieve the symptoms and prevent secondary infections. This may include pain relievers, antibiotics, and fluids.
Question 4: How can orf be prevented?
The best way to prevent orf is to vaccinate goats and sheep against the virus. There are several different vaccines available, and they are typically administered twice, 2-3 weeks apart. In addition to vaccination, good biosecurity practices can help to reduce the risk of infection. This includes isolating new animals, disinfecting equipment, and providing clean food and water.
Question 5: Is orf a zoonotic disease?
Yes, orf is a zoonotic disease, which means that it can be transmitted from animals to humans. In humans, orf causes a similar skin infection, which can be painful and itchy. However, the infection is typically mild and self-limiting.
Question 6: What should I do if I think my animal has orf?
If you think your animal has orf, it is important to contact your veterinarian immediately. Your veterinarian will be able to diagnose the disease and recommend the best course of treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to reduce the severity of the disease and prevent secondary infections.
Orf is a serious disease that can have a significant impact on the health of goats and sheep. However, by following good biosecurity practices and vaccinating your animals, you can help to reduce the risk of infection. If you think your animal has orf, it is important to contact your veterinarian immediately.
Orf: A Rare And Devastating Disease In Goats And Sheep
Tips
Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for effective Orf management. Here are several recommended tips to help prevent and control outbreaks:
Tip 1: Implement biosecurity measures
Restrict contact between animals from different flocks, disinfect equipment and vehicles used for transportation, and isolate infected animals promptly.
Tip 2: Vaccinate susceptible animals
Vaccinating young animals and pregnant females before lambing or kidding can significantly reduce the severity and incidence of outbreaks.
Tip 3: Control vectors
Prevent flies and other insects from spreading the virus by using repellents, insecticides, and proper manure management.
Tip 4: Disinfect contaminated areas
Thoroughly clean and disinfect areas where infected animals have been present, including pens, equipment, and vehicles, using appropriate disinfectants.
Tip 5: Isolate and treat infected animals
Separate infected animals from the rest of the flock, provide supportive care such as antibiotics and pain relievers, and consult with a veterinarian promptly.
Tip 6: Monitor and test
Regularly monitor animals for signs of Orf and consider testing suspected cases to confirm diagnosis and prevent further spread.
Tip 7: Report outbreaks
Notify veterinary authorities and animal health organizations about outbreaks to facilitate prompt investigation and containment measures.
Tip 8: Educate and train
Provide education and training for farm workers and livestock owners to enhance understanding of Orf symptoms, transmission, and control measures.
By following these tips, farmers and livestock owners can effectively prevent and control Orf outbreaks, protecting the health and productivity of their animals.
Orf: A Rare And Devastating Disease In Goats And Sheep
Orf, a rare and contagious disease primarily affecting goats and sheep, constitutes a significant concern due to its highly transmissible nature and severe impacts on animal health and productivity. To comprehend the complexities of Orf, examining key aspects such as its rarity, transmission modes, clinical signs, control measures, and economic implications is essential.
- Rarity: Orf is an uncommon disease, with sporadic outbreaks occurring worldwide.
- Transmission: The virus causing Orf spreads primarily through direct contact with infected animals or contaminated surfaces.
- Clinical Signs: Characteristic lesions, known as "scabby mouth," develop around the mouth, nostrils, and feet, causing discomfort and difficulty feeding.
- Control Measures: Vaccination and strict biosecurity practices are the primary means of controlling Orf outbreaks.
- Economic Impact: Outbreaks disrupt farming operations, leading to reduced productivity, increased veterinary expenses, and potential trade restrictions.
- Diagnostic Challenges: Distinguishing Orf from other diseases with similar clinical signs, like foot-and-mouth disease, can be challenging, demanding meticulous diagnostic procedures.
Understanding these key aspects is crucial for effective management and prevention of Orf. Early detection, prompt implementation of control measures, and enhanced biosecurity practices are paramount in safeguarding goat and sheep populations from the devastating impacts of this rare yet highly contagious disease.
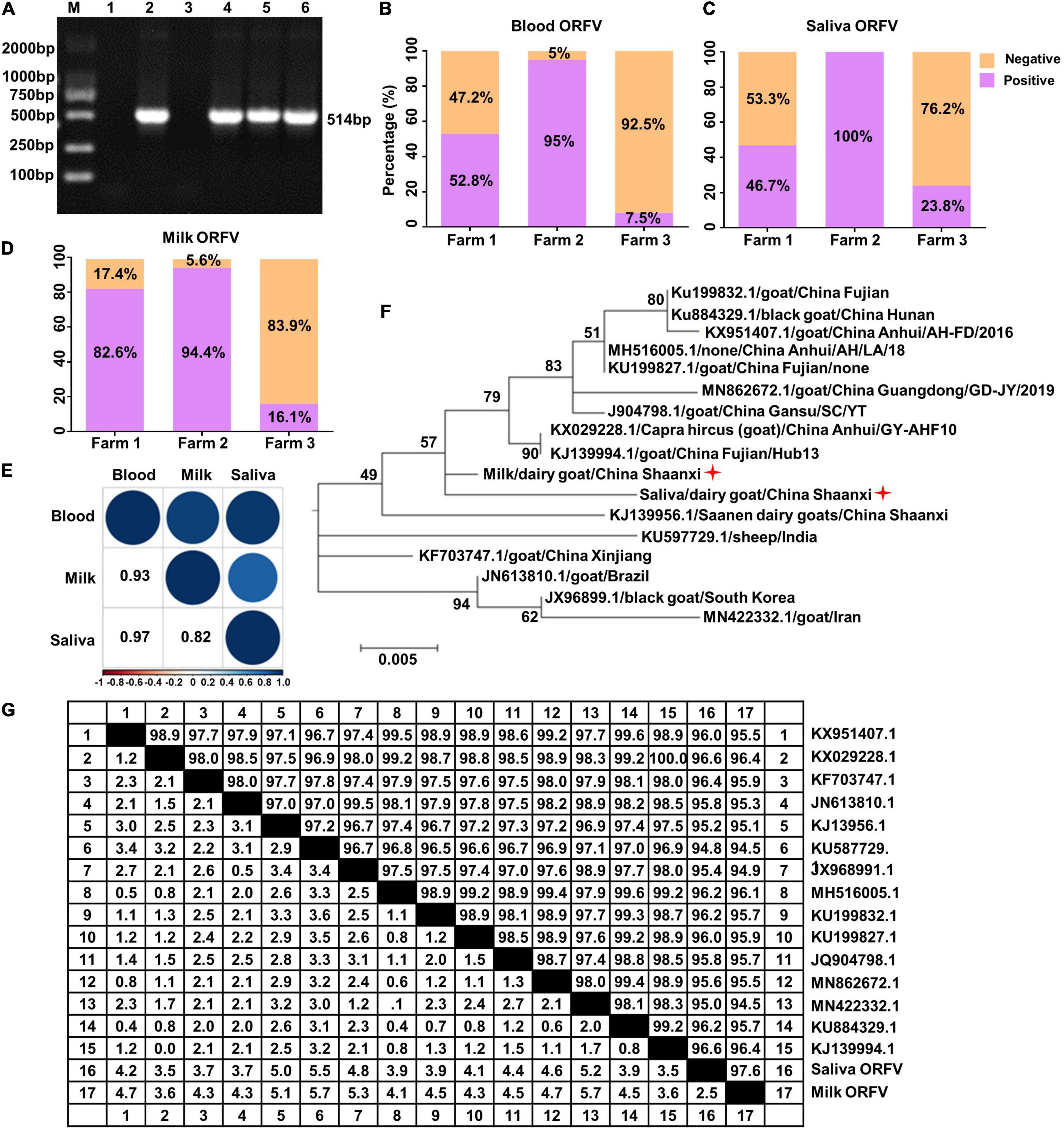
Frontiers | Orf Virus Detection in the Saliva and Milk of Dairy Goats - Source www.frontiersin.org
Orf: A Rare And Devastating Disease In Goats And Sheep
ORF is a contagious disease that affects goats and sheep. It is caused by a virus that is spread through contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids. ORF can cause a variety of symptoms, including fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, and sores on the mouth, nose, and feet. In severe cases, ORF can be fatal.

Ectomia Cenno All'ectomia Contagiosa Nella Bocca Della Capra . Medicina - Source it.dreamstime.com
ORF is a serious disease that can have a devastating impact on the health of goats and sheep. It is important for farmers to be aware of the signs and symptoms of ORF and to take steps to prevent the disease from spreading. There is no specific treatment for ORF, but supportive care can help to improve the chances of survival.
Preventing ORF is the best way to protect goats and sheep from this devastating disease. Farmers should vaccinate their animals against ORF and take steps to prevent contact with infected animals.
Conclusion
ORF is a rare but devastating disease that can affect goats and sheep. It is important for farmers to be aware of the signs and symptoms of ORF and to take steps to prevent the disease from spreading. There is no specific treatment for ORF, but supportive care can help to improve the chances of survival.
Preventing ORF is the best way to protect goats and sheep from this devastating disease. Farmers should vaccinate their animals against ORF and take steps to prevent contact with infected animals.

EmoticonEmoticon